Treatments
- Treatments
- Hysteroscopy
- Hysteroscopic Adhesiolysis
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Infertility
- PCOS
- Endometriosis
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Female Cancer Screening & Vaccination
- MTP - Govt Recognized
- Pre Conceptional & Post Natal Counselling
- Pregnancy
- Maternity & High Risk Pregnancy
- Contraception & Family Planning (Govt Recognized)
- Hysterectomy
- Sonography
Laparoscopic Surgery
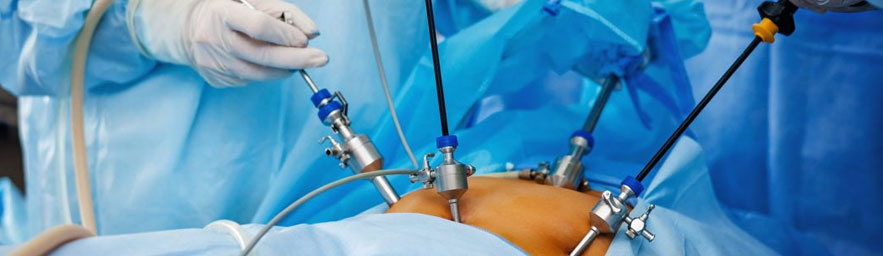
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, is a surgical procedure used to examine and operate on the organs inside the abdomen. This technique involves making small incisions through which a laparoscope—a long, thin tube with a high-intensity light and a high-resolution camera—is inserted. The camera transmits images to a monitor, allowing surgeons to see inside the abdomen in real-time without making large incisions. Laparoscopy is commonly used for diagnosing and treating conditions such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, and various abdominal and pelvic cancers. It can also be used for procedures like gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and appendectomy. The benefits of laparoscopy include reduced pain and bleeding, shorter recovery times, and smaller scars compared to traditional open surgery. Despite its minimally invasive nature, it requires specialized skills and training to perform effectively and safely.
Laparoscopy is performed under general anaesthesia, so you'll be unconscious during the surgery and won't feel pain. Laparoscopic surgery has advantages over traditional surgery including: much smaller scars. reduced pain.
